Flanges
First Distributors offers a wide range of flanges and can typically provide the following for same-day or next-day delivery. Large quantites, custom sizes, and special alloys (Alloy 20, Monel, Hastelloy, Inconel, Titanium, etc) may be subject to a longer lead time for delivery.
Items Typically on the shelf:
| Size Range: | 1/2" - 48" Diameter |
| Types: | Slip On, Socket Weld, Weld Neck, Threaded, Blind, Lap Joint, Long Weld Neck, Orifice/Orifice Plate, and API Flange |
| Class: | 150 through 2500 |
| Carbon Steel: | A105 |
| Stainless Steel: | 304, 316 |
Those Potentially Requiring A Lead Time:
| Carbon Steel: | A350, A694 |
| Stainless Steel: | 310, 321, 347 |
| Exotic Alloys: | A20, C276, Duplex 2205, Duplex 2507, AL6XN, A200, A600, Monel, Inconel, Incoloy 800, Incoloy 825, Aluminum, Titanium |
A Guide To Flange Materials
Carbon & Stainless Flanges
- Standard Carbon Steel Flanges (A105): ASTM A105 is an ASTM specification dealing with forged carbon steel piping components
- Stainless Steel Flanges (A182): This specification covers forged or rolled alloy and stainless steel (304, 304L, 316L) flanges. This spec also covers other alloys including chrome (i.e. A182 F11)
- High Yield Flanges (F694): ASTM A694 is the standard specification to cover carbon and alloy steel forgings for pipe flanges, fitting, valves and other parts for high-pressure transmission service. Applications include, but are not limited to, in wellhead and Christmas-tree manifold equipment in oil and gas industry. The two numbers in each grade indicate the yield strength requirements, in ksi.
- Low-Temp Flanges (A350): This specification covers several grades of carbon and low alloy steel forged or ring-rolled flanges (LF2 in low-temp applications).
Wedge Gate
- Alloy 20
- Duplex 2205
- Super Duplex 2507
- Hastelloy C276
- Incoloy 800
- Incoloy 825
- Monel 400
- Inconel 625
Connection Types Explained (Type Of Flange)
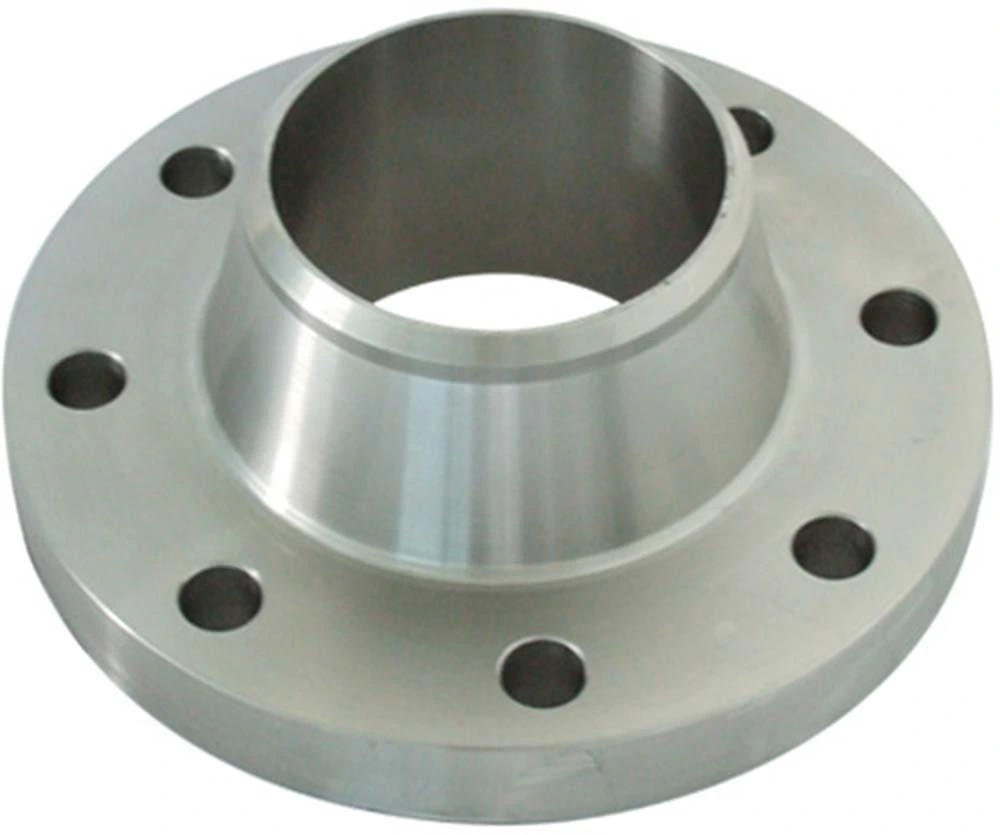

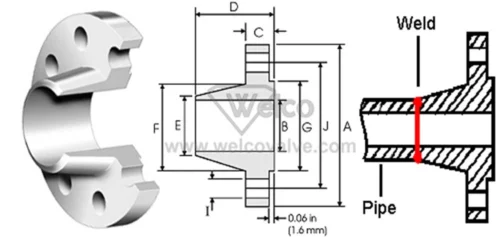
Weld neck
The bore of the pipe and flange match in order to reduce turbulence and erosion, thus making it the strongest connection type and the most favorable in critical applications.
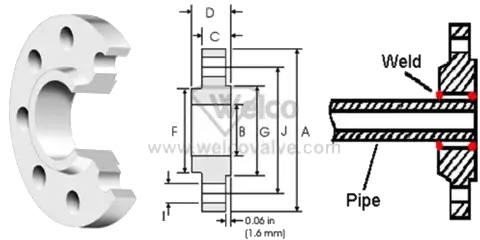
Slip-on
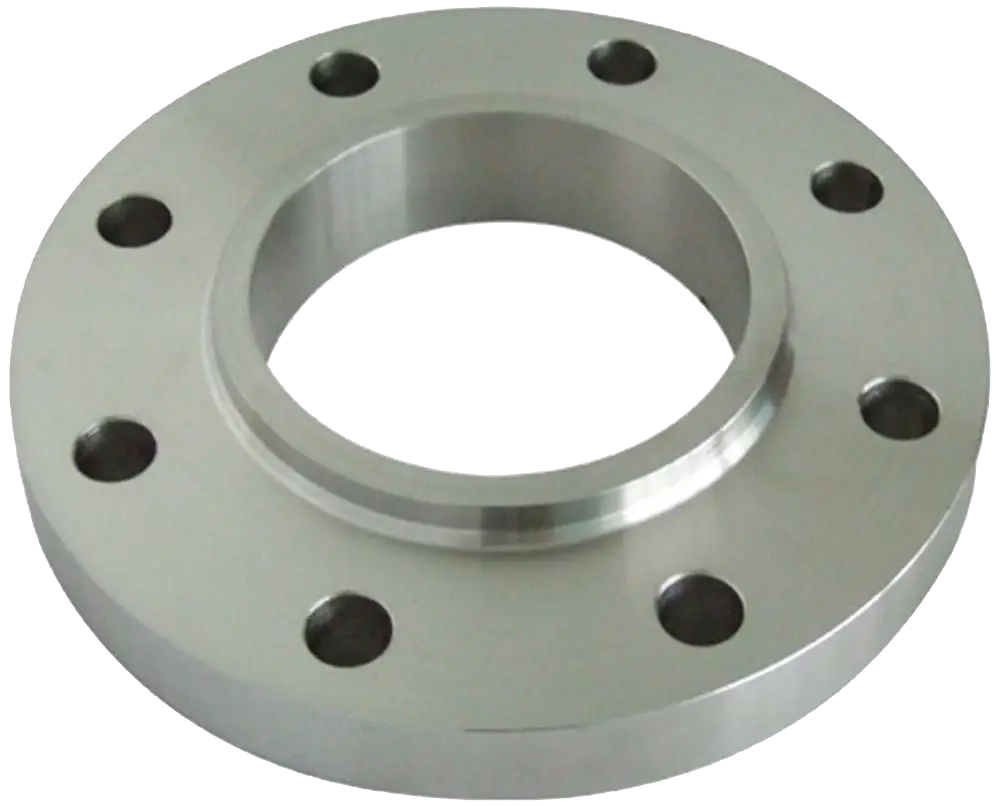


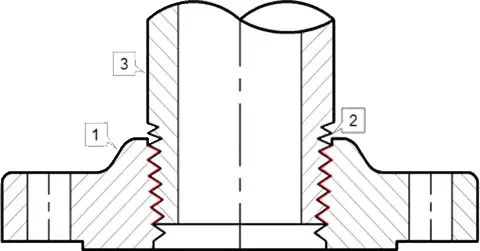
Threaded
Blind

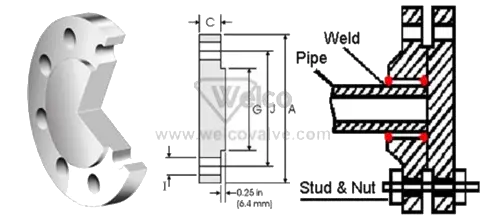

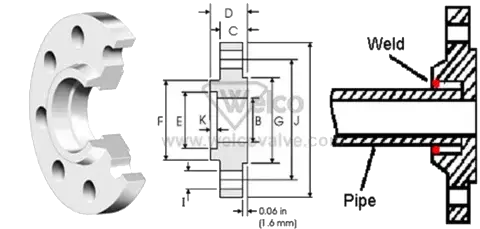
Socket weld
The bore of the pipe and flange match, thus providing good flow characteristics.
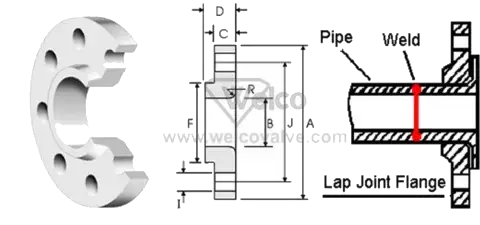
Lap joint
Favored in low pressure applications because it is easily assemble and aligned. These flanges look very similar to a slip on, but the are distinguished by the rounded interior edge of the flange face.
To reduce cost these flanges can be supplied without a hub and/or in treated, coated carbon steel

Pressure Class Information
These classes include: 150 LBS, 300 LBS, 400 LBS, 600 LBS, 900 LBS, 1500 LBS, and 2500 LBS.
A higher class rating will increase the weight, height, face, and often times change the stud bolts required for installation. Precise dimensions for each flange, by class, can be viewed in our technical flange specification page.
Bolt chart for flanges by class can be seen here
Face Types Available

Raised Face
Primary purpose is to concentrate more pressure on a smaller gasket area and thereby increase the pressure containment capability of the joint, creating a more secure connection.
Full face
Often used in applications where the mating flange or fitting is made from a casting since relatively brittle cast iron requires a full-face contact point.


Ring-type face
Series A Vs Series B
For flanges above 24", the flange must be specified for either series A or series B. These are competing specifications that were brought together in B16.47. ASME has incorporated most of the MSS-SP44 spec into B16.47 Series A and most of the API 605 spec into B16.47 series B. Weld necks and blinds are covered under these two specs. For slip-ons over 24”, you must refer to either Industry Standard or Boiler Code flanges.
Manufacturers Commonly Available
We can provide flanges from a large selection of manufacturers, with several of them listed below.
| Manufacturer | Country |
|---|---|
| Bebitz | Germany |
| Buffalo Flange | USA |
| DL Flange | USA |
| Galperti Flange | USA/Italy |
| Goodluck Steel | India |
| Kerkau | USA |
| Metalfar | Italy |
| National Flange | USA |
| Technoforge | Italy |
| Trilad | USA |
| Ulma | Spain |
| Viraj | India |
| Weldbend | USA |
